Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, most frequently in the legs. If left unchecked, these clots can dislodge and travel to the lungs, leading to a pulmonary embolism (PE), which can be fatal. While anyone can develop DVT, certain risk factors make some individuals more susceptible than others. Understanding these factors and implementing preventive measures is essential for reducing the risk of developing this serious condition. In this article, we will explore effective strategies and tips for preventing DVT, empowering readers with knowledge to safeguard their health.
Prevention Strategies for Deep Vein Thrombosis
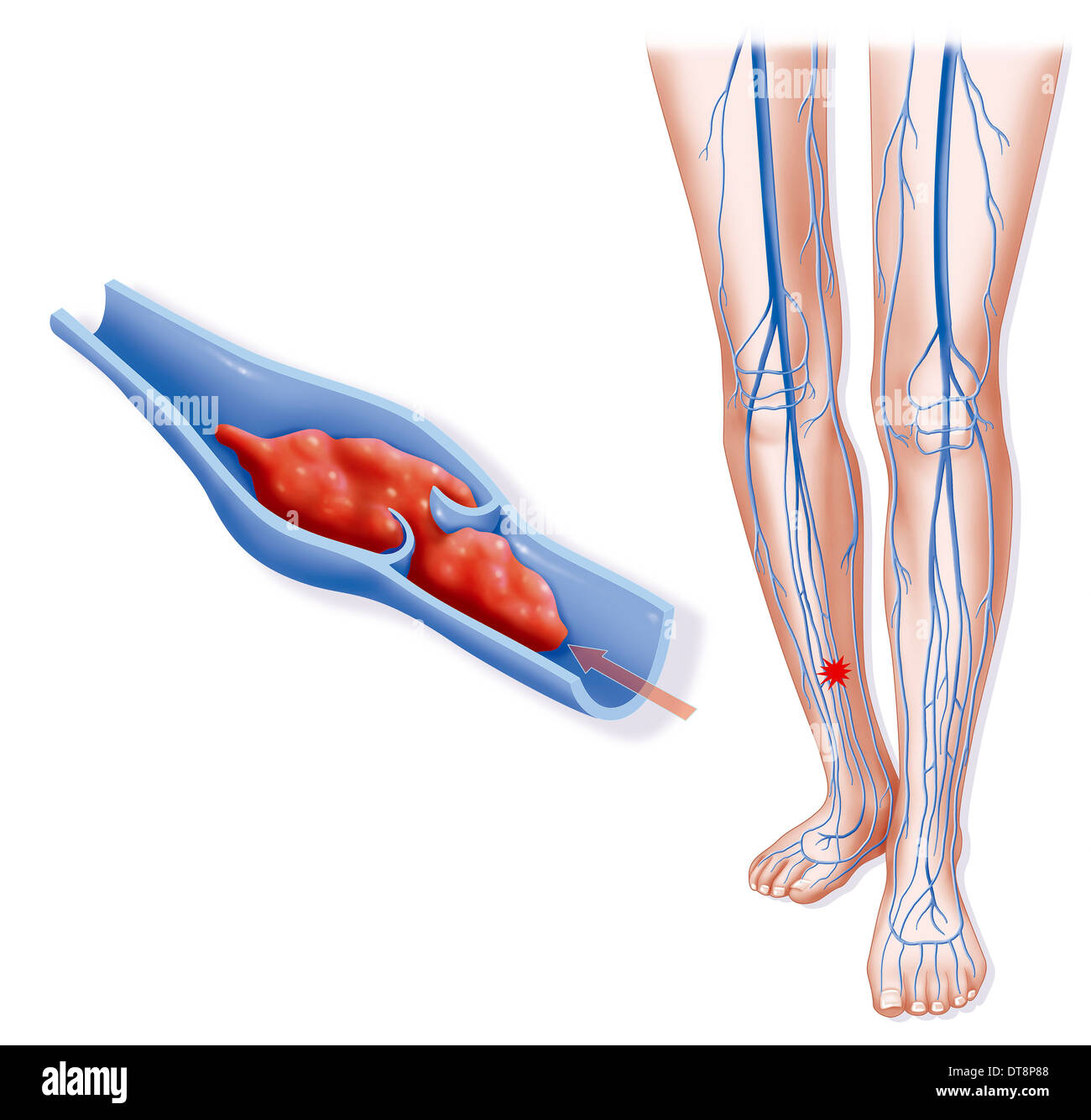
Preventing DVT requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, proactive measures, dietary considerations, and awareness of signs and symptoms. By taking actionable steps toward prevention, individuals can significantly reduce their likelihood of developing this dangerous condition. Below, we delve into various strategies and tips to help mitigate the risks associated with deep vein thrombosis.
Lifestyle Modifications
Staying Active
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy blood circulation and preventing the formation of blood clots. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise on most days of the week. Activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling not only improve cardiovascular health but also promote better blood flow in the legs. For individuals with mobility limitations or those who are recovering from surgery, gentle exercises like stretching and leg lifts can be beneficial in promoting circulation without overexertion.
Incorporating movement into your daily routine is vital, especially if you lead a sedentary lifestyle due to work or other commitments. Consider taking short breaks every hour to stretch or walk around the office or home. Simple actions, such as standing up while talking on the phone or using the stairs instead of the elevator, can add up and contribute to overall physical activity levels.
Hydration
Proper hydration is another fundamental aspect of preventing DVT. Drinking an adequate amount of fluids, particularly water, helps maintain optimal blood viscosity, preventing it from becoming too thick and sticky. Dehydration can lead to reduced blood flow and increase the risk of clot formation. Aim to consume at least eight glasses of water per day, adjusting your intake based on activity levels, climate, and individual needs.
In addition to drinking water, incorporating hydrating foods into your diet can further enhance your hydration efforts. Fruits and vegetables, such as watermelon, cucumbers, and oranges, are excellent sources of hydration and provide essential vitamins and minerals that support overall health. Avoid excessive consumption of caffeinated beverages and alcohol, as they can contribute to dehydration.
Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for reducing the stress on your veins and improving blood flow. Excess weight can compress veins, impairing circulation and increasing the risk of DVT. A balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight. Additionally, engaging in regular physical activity contributes to weight management and overall well-being.
For those struggling with weight loss, consider working with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to develop a personalized meal plan and exercise regimen. Small, gradual changes to eating habits and physical activity levels can lead to sustainable weight management and improved health outcomes.
Medical Interventions
Blood Thinners
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are medications used to prevent blood clots from forming and growing. They are often prescribed for high-risk individuals, such as those undergoing major surgeries or those with specific medical conditions. Blood thinners work by disrupting the blood clotting process, thereby reducing the risk of DVT.
It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding anticoagulant use, as these medications can interact with other drugs and have potential side effects. Regular monitoring may be required to ensure the effectiveness of blood thinners and to adjust dosages accordingly. If you have any concerns about taking these medications, don’t hesitate to discuss them with your doctor.
Compression Stockings Therapy
Compression stockings serve as a practical and effective preventive measure for individuals at risk of DVT. These specialized stockings apply graduated pressure to the legs, promoting blood flow and reducing swelling. Compression therapy is particularly valuable during long flights or periods of immobility, as it helps counteract the effects of prolonged sitting or standing.
When selecting compression stockings, consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate level of compression for your needs. It’s essential to wear these stockings correctly and consistently for optimal benefits. Compression devices are also available for air travel, designed specifically for individuals at high risk of DVT.
Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Filter
For patients who cannot tolerate blood thinners or have a history of recurrent DVT, an inferior vena cava (IVC) filter may be recommended. This small device is inserted into the vena cava, the largest vein in the body, to catch any blood clots that may travel from the legs to the lungs. The IVC filter serves as a preventive measure against pulmonary embolism and is typically reserved for individuals with significant risk factors.
As with any medical intervention, discussing the potential benefits and risks of IVC filters with your healthcare provider is essential. Monitoring and follow-up care are necessary to ensure the filter remains effective and functions properly over time.
Proactive Measures
Regular Medical Checkups
Routine checkups with your healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring your health and identifying any factors that may require intervention. During these visits, be sure to discuss any concerns related to DVT and inform your doctor of your family history, lifestyle, and any medical conditions that may increase your risk. Early detection and intervention can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing DVT.
Additionally, if you have recently undergone surgery or have experienced extended periods of immobility, schedule follow-up appointments to evaluate your recovery and assess any potential complications. Your healthcare provider can offer personalized recommendations for preventative measures based on your individual circumstances.
Know Your Family History
Understanding your family history is critical when assessing your risk for DVT. If you have relatives who have experienced DVT or pulmonary embolism, it’s essential to communicate this information to your healthcare provider. Genetic predisposition can play a substantial role in an individual’s risk for blood clot formation.
Awareness of your genetic background allows for proactive management of your health. Your doctor may recommend specific preventive measures tailored to your risk profile, such as increased surveillance, lifestyle modifications, or even genetic testing in certain cases.
Be Aware of Travel Risks
Traveling, particularly on long-haul flights or road trips, can significantly increase the risk of DVT due to prolonged immobility. Being proactive before and during travel can help mitigate these risks. Prior to embarking on a journey, ensure you are hydrated, wear comfortable clothing, and consider wearing compression stockings if you are at heightened risk for DVT.
During travel, take breaks to stand, stretch, and walk around every hour. Simple leg exercises, such as ankle pumps and calf raises, can promote circulation even while seated. If traveling by plane, consider booking an aisle seat to allow easier access for movement throughout the flight.
Dietary Considerations
Fiber-Rich Diet
A diet high in fiber can improve digestion and reduce the risk of constipation, which can indirectly contribute to DVT risk. Constipation can lead to straining during bowel movements, which puts added pressure on the abdominal veins and can hinder blood flow. Incorporating fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes into your meals can help promote regular bowel movements and support overall digestive health.
In addition to its digestive benefits, a fiber-rich diet may aid in weight management and support heart health, making it a valuable component of a comprehensive DVT prevention strategy. Aim to gradually increase your fiber intake, along with adequate hydration, to avoid gastrointestinal discomfort.
Healthy Fats
Incorporating healthy fats into your diet can also play a role in preventing DVT. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in oily fish, nuts, and seeds, possess anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce the risk of clot formation. Research suggests that omega-3 fatty acids can improve endothelial function, which is essential for maintaining healthy blood vessels and promoting normal blood flow.
Consider adding sources of healthy fats to your meals, such as salmon, walnuts, chia seeds, and avocados. A balanced diet enriched with these nutrient-dense foods can support cardiovascular health while contributing to overall wellness.
Hydration
As previously discussed, proper hydration is vital for maintaining healthy blood flow and preventing DVT. In addition to drinking water, consuming hydrating foods and avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol are key components of maintaining adequate fluid levels. Staying well-hydrated supports blood viscosity and enhances overall circulation, thereby reducing the likelihood of clot formation.
Additional Tips for Prevention
Wear Loose-Fitting Clothing
Choosing loose-fitting clothing can support healthy blood flow and reduce the risk of DVT. Tight clothing, particularly around the waist and legs, can constrict veins and impede circulation. Opt for comfortable, breathable fabrics that allow for unrestricted movement, especially during long periods of sitting or standing.
When dressing for travel, avoid wearing tight belts or socks, as these can exacerbate venous compression. Instead, select clothing that prioritizes comfort to promote healthy circulation during your journeys.
Avoid Crossing Your Legs for Long Periods
Crossing your legs can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of DVT, particularly if done for extended periods. When sitting, try to keep both feet flat on the floor or elevate your legs periodically to facilitate proper blood circulation. If you find yourself spending long hours sitting at work or while traveling, integrate regular movement into your routine to encourage healthy blood flow.
Stretch Regularly
Engaging in regular stretching exercises can help improve circulation and enhance flexibility, reducing the likelihood of DVT. Focus on stretches that target the legs and ankles, such as calf stretches, hamstring stretches, and ankle circles. Aim to incorporate stretching into your daily routine, particularly if you experience long periods of sitting or standing.
Listening to Your Body
Being attuned to changes in your body is vital for early detection of potential problems. Pay attention to any unusual symptoms in your legs, such as swelling, pain, redness, or warmth, as these could indicate the presence of DVT. If you notice any concerning signs, contact your healthcare provider promptly for evaluation and guidance.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Recognizing the warning signs of DVT is crucial for seeking timely medical attention. The most common symptoms include pain or tenderness in the affected leg, swelling, redness or discoloration, and warmth to the touch. However, it’s important to note that not everyone with DVT exhibits all these symptoms.
If a clot dislodges and travels to the lungs, it can result in a pulmonary embolism (PE), which presents additional symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing, and rapid heart rate. If you experience any of these symptoms, particularly in conjunction with known risk factors for DVT, seek immediate medical assistance.
Conclusion
Preventing deep vein thrombosis is essential for safeguarding your health and well-being. By understanding the risk factors associated with DVT and adopting effective prevention strategies, individuals can significantly reduce their likelihood of developing this potentially life-threatening condition. Lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, proactive measures, dietary considerations, and awareness of signs and symptoms are all critical components of a comprehensive approach to DVT prevention.
Taking proactive steps, staying informed, and consulting with healthcare providers when necessary can empower individuals to manage their health effectively. Remember, early detection and intervention are vital in preventing complications associated with DVT. If you have concerns or questions regarding your risk for DVT, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and support.


